Cold allodynia, pain in response to cooling, occurs during or within hours of oxaliplatin infusion and is thought to arise from a direct effect of...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 521
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2013-09-30 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:11
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[prim_key] => 1019
[id_lang] => 1
[title] => An animal model of oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia reveals a crucial role for
[paragraph] => An animal model of oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia reveals a crucial role for Nav1.6 in peripheral pain pathways
[content] => Authors
Jennifer R. Deuis, Katharina Zimmermann, Andrej A. Romanovsky, et al.
Lab
University of Queenland, Australia
Journal
PAIN Volume 154, Issue 9
Abstract
Cold allodynia, pain in response to cooling, occurs during or within hours of oxaliplatin infusion and is thought to arise from a direct effect of oxaliplatin on peripheral sensory neurons. To characterize the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying acute oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia, we established a new intraplantar oxaliplatin mouse model that rapidly developed long-lasting cold allodynia mediated entirely through tetrodotoxin-sensitive Nav pathways. Using selective inhibitors and knockout animals, we found that Nav1.6 was the key isoform involved, while thermosensitive transient receptor potential channels were not involved. Consistent with a crucial role for delayed-rectifier potassium channels in excitability in response to cold, intraplantar administration of the K+-channel blocker 4-aminopyridine mimicked oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia and was also inhibited by Nav1.6 blockers. Intraplantar injection of the Nav1.6 activator Cn2 elicited spontaneous pain, mechanical allodynia, and enhanced 4-aminopyridine-induced cold allodynia. These findings provide behavioural evidence for a crucial role of Nav1.6 in multiple peripheral pain pathways including cold allodynia.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Electronic Von Frey 4 (BIO-EVF4),Electronic Von Frey 5 with embedded camera (BIO-EVF5)
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => http://www.painjournalonline.com/article/S0304-3959(13)00271-6/abstract
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => an-animal-model-of-oxaliplatin-induced-cold-allodynia-reveals-a-crucial-role-for-nav1-6-in-peripheral-pain-pathways
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 1088
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 521
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Miscellaneous research domains
[link_rewrite] => Miscellaneous-research-domains
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => An animal model of oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia reveals a crucial role for Nav1.6 in [...]
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[1859] => Array
(
[name] => Electronic Von Frey - Wireless
[description_short] => A quick solution to determine the mechanical sensitivity threshold in rodents (mice and rats). Now wireless, to be free from annoying cables!
This precise and easy-to-use electronic instrument is a must-have reference for your research in analgesia, nociception, neuro-pathologies and post-operative pain.


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/preprod.bioseb.com/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://preprod.bioseb.com/en/pain-mechanical-allodynia-hyperalgesia/1859-electronic-von-frey-4.html
)
[1860] => Array
(
[name] => Electronic Von Frey 5 with embedded camera
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/preprod.bioseb.com/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://preprod.bioseb.com/en/pain-mechanical-allodynia-hyperalgesia/1859-electronic-von-frey-4.html
)
[1860] => Array
(
[name] => Electronic Von Frey 5 with embedded camera
[description_short] => As an electronic version of the classical Von Frey Filaments esthesiometer (or aesthesiometer), the latest evolution of Bioseb's Electronic Von Frey instrument for determining the mechanical sensitivity threshold in rodents (rats and mice) is a must-have instrument for your reseach on hyperalgesia and allodynia. By measuring and recording the force at which the animal exhibits a paw withdrawal reflex, pathologies related to sensory response and hyper- or hypo-aesthesia can be studied.
The EVF5 includes an embedded camera inside the stimulator handle and a new, dedicated software revolutionizing the experimental process.


[thumb] => 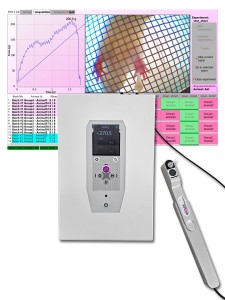 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/preprod.bioseb.com/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://preprod.bioseb.com/en/pain-mechanical-allodynia-hyperalgesia/1860-electronic-von-frey-5-with-embedded-camera.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/preprod.bioseb.com/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://preprod.bioseb.com/en/pain-mechanical-allodynia-hyperalgesia/1860-electronic-von-frey-5-with-embedded-camera.html
)
)
)
1 Read more 
