ntroduction: Several studies have suggested that diet, especially one enriched in microbiota-fermented fibers or fat, regulates behavior. The...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 1358
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2021-01-11 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:12
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[prim_key] => 2905
[id_lang] => 1
[title] => Dietary fibers and proteins modulate behavior via the activation of intestinal g
[paragraph] => Dietary fibers and proteins modulate behavior via the activation of intestinal gluconeogenesis
[content] => Authors
F Sinet, J Zemdegs, M Soty et al
Lab
INSERM U1213, F-69008Lyon, France
Journal
Neuroendocrinology
Abstract
ntroduction: Several studies have suggested that diet, especially one enriched in microbiota-fermented fibers or fat, regulates behavior. The underlying mechanisms are currently unknown. We previously reported that certain macronutrients (fermentable fiber and protein) regulate energy homeostasis via the activation of intestinal gluconeogenesis (IGN), which generates a neural signal to the brain. We hypothesized that these nutriments might control behavior using the same gut-brain circuit. Methods: Wild-type and IGN-deficient mice were fed chow or diets enriched in protein or fiber. Changes in their behavior were assessed using suited tests. Hippocampal neurogenesis, extracellular levels of serotonin and protein expression levels were assessed by immunofluorescence, in vivo dialysis or western-blotting respectively. Rescue of IGN was performed by infusing glucose in the portal vein of IGN-deficient mice. Results: We show here that both fiber- and protein-enriched diets exert beneficial actions on anxiety-like and depressive-like behaviors. These benefits do not occur in mice lacking IGN. Consistently, IGN-deficient mice display hallmarks of depressive-like disorders, including decreased hippocampal neurogenesis, basal hyperactivity and deregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, which are associated with increased expression of the precursor of corticotropin releasing hormone in the hypothalamus and decreased expression of the glucocorticoid receptor in the hippocampus. These neurobiological alterations are corrected by portal glucose infusion mimicking IGN. Conclusion: IGN translates nutritional information allowing the brain to finely coordinate energy metabolism and behavior.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Elevated Plus Maze : EPM3C - 3 clicks only ! (BIO-EPM3C),Forced Swimming Test: New FST DUAL SENSOR (BIO-FST-DSM)
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => https://doi.org/10.1159/000514289
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => dietary-fibers-and-proteins-modulate-behavior-via-the-activation-of-intestinal-gluconeogenesis
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 1484
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 1358
[categories] => Array
(
[60] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 60
[title] => Cognitive performance
[link_rewrite] => Cognitive-performance
)
[82] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 82
[title] => Food intake / Nutrition
[link_rewrite] => Food-intake-Nutrition
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => Dietary fibers and proteins modulate behavior via the activation of intestinal gluconeogenesis
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[1576] => Array
(
[name] => Elevated Plus Maze : EPM3C - 3 clicks only !
[description_short] => NEW ! A complete (hardware + software), dedicated and automated solution for the Elevated Plus Maze test, featuring unprecedented simplicity to run these very popular protocols. A user-friendly and innovative solution for your research on anxiety, depression and the screening of anxiolytic drugs.
[thumb] => 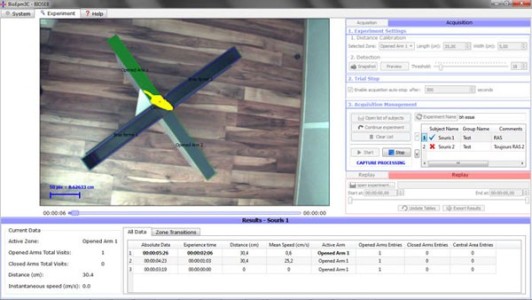 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/preprod.bioseb.com/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://preprod.bioseb.com/en/anxiety-depression-disorder/1576-elevated-plus-maze-epm3c-3-clicks-only-.html
)
[973] => Array
(
[name] => Forced Swimming Test: New FST DUAL SENSOR
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/preprod.bioseb.com/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://preprod.bioseb.com/en/anxiety-depression-disorder/1576-elevated-plus-maze-epm3c-3-clicks-only-.html
)
[973] => Array
(
[name] => Forced Swimming Test: New FST DUAL SENSOR
[description_short] => The new Forced Swimming Test system from Bioseb uses a dual approach:
Combining a double input from vibrations and video,
the TYC (Train-Your-Computer) algorithm compares both inputs to determine the animal's behavior in real time, making results completely operator-independent.
Experiment manager, analysis module, replay possibilities and the TYC algorithm are some of the features that make FST DUAL SENSOR a very innovative and easy to use instrument for both mice or rats studies (up to 4 animals can be tested at a time), based on the famous Porsolt Test, or "behavioral despair" test


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/preprod.bioseb.com/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://preprod.bioseb.com/en/anxiety-depression-disorder/973-forced-swimming-test-new-fst-dual-sensor.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/preprod.bioseb.com/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://preprod.bioseb.com/en/anxiety-depression-disorder/973-forced-swimming-test-new-fst-dual-sensor.html
)
)
)
1 Read more 
