Preclinical pain assessment remains a key step for the development of new and potent painkillers. Significant progress in pain evaluation has been...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 417
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2011-09-01 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:11
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[prim_key] => 830
[id_lang] => 2
[title] => Weight bearing evaluation in inflammatory- neuropathic and cancer chronic pain i
[paragraph] => Weight bearing evaluation in inflammatory, neuropathic and cancer chronic pain in freely moving rats
[content] => Authors
Tétreault P, Dansereau MA, Doré-Savard L, Beaudet N, Sarret P.
Lab
Department of Physiology and Biophysics, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada.
Journal
Physiol Behav.
Abstract
Preclinical pain assessment remains a key step for the development of new and potent painkillers. Significant progress in pain evaluation has been achieved with the development of non-reflexive tools. Seeking efficient and clinically relevant devices for pain-related quality of life assessment, we evaluated a new Dynamic Weight Bearing (DWB) device based on pressure captors in three different preclinical chronic pain models. Inflammatory (CFA), neuropathic (CCI) and bone cancer pain (femoral tumor) models were evaluated in Sprague Dawley rats for mechanical allodynia using dynamic von Frey for pain-related behaviors and DWB for discomfort. We observed similar impairment patterns in all of the models for both von Frey (allodynia) and DWB (weight balance) during the complete observation period, starting at day 3 in CCI- and CFA-affected limbs and at day 14 in bone cancer-afflicted rats, indicating that the DWB could be a useful tool for supporting pain assessment. Interestingly, we demonstrated that the main compensation, when animals experienced pain, was seen in the forepaws, ranging from 46% to 69% of increased load compared to normal. Other pain-related coping behaviors were also measured, such as the time spent on each paw and the contact surface. Our results revealed that CFA, CCI and cancerous rats decreased the use of their ipsilateral hind paws by 30% and showed a 50% reduction in paw surface pressed against the floor. In conclusion, this new device improves methods for preclinical evaluation of discomfort and quality of life proxies and could be helpful in screening putative analgesics.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 (BIO-DWB-DUAL)
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21620878
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => weight-bearing-evaluation-in-inflammatory--neuropathic-and-cancer-chronic-pain-in-freely-moving-rats
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 1055
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 417
[categories] => Array
(
[90] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 90
[title] => Cancer
[link_rewrite] => Cancer
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => Weight bearing evaluation in inflammatory, neuropathic and cancer chronic pain in freely moving rats
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[1216] => Array
(
[name] => Distribution Pondérale Dynamique 2.0
[description_short] => Un système permettant l'analyse de la posture des animaux par la répartition du poids sur chacune des 4 pattes. Le DWB est un test unique dans l'étude de nombreux modèles de douleurs, principalement non évoquée , neuropathique ou encore inflammatoire ainsi que pour les études sur l'osthéoarthrite et divers affections du SNC.
Le nouvelle version DWB2 intègre une nouvelle interface logiciel plus simple avec gestion des listes d'animaux ainsi que de nouveaux algorithmes d'analyse automatique de la posture.


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/preprod.bioseb.com/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://preprod.bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Module Postural Additionnel
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/preprod.bioseb.com/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://preprod.bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Module Postural Additionnel
[description_short] => Étendez votre analyse grâce à des calculs posturaux et locomoteurs avancés
Le système de Distribution Pondérale Dynamique (DWB2) de BIOSEB s’enrichit avec l'ajout du Module Postural. Ce complément logiciel optionnel améliore l’analyse standard de la répartition du poids en intégrant des nouveaux calculs conçus pour l’étude de la posture, de la locomotion et de l’activité des animaux.
Développé en collaboration avec le laboratoire du Dr. Tighilet de l’Université Aix-Marseille - CNRS, le Module Postural améliore votre DWB2 en fournissant des paramètres précieux pour les recherches sur la douleur, les troubles vestibulaires et les maladies neurodégénératives.


[thumb] => 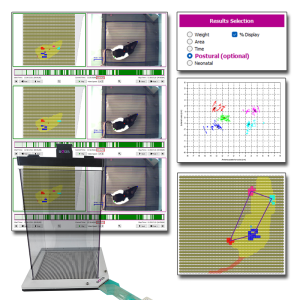 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/preprod.bioseb.com/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://preprod.bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-module-postural-additionnel.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/preprod.bioseb.com/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://preprod.bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-module-postural-additionnel.html
)
)
)
1 En lire plus 
